TORREFIED BIOMASS PELLETS

TORREFIED BIOMASS PELLETS
As global climate goals tighten and industrial emissions are observe, heavy industries across India are rethinking how they generate heat and energy. Boilers, thermic fluid heaters, and furnaces—traditionally fired by coal, furnace oil (FO), or diesel—are responsible for significant carbon emissions, air pollution, and fuel costs.
Hence, one need to seek for renewable fuel, especially solid biomass fuel with the fuel properties equivalent to existing fossil fuel. Enter torrefied biomass—a cleaner, high-performance biofuel that offers a practical and scalable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. With its coal-like characteristics and renewable nature, torrefied biomass is now emerging as one of the most promising solutions for industrial heating systems.

1. What Is Torrefied Biomass and How Is It Made?
Torrefied biomass is produced by heating biomass (like wood chips, agri-waste, or sawdust) in absence of oxygen—a process called torrefaction.
What is Torrefaction
Biomass torrefaction is a thermal process used to produce high-grade solid biofuels from various streams of woody biomass or agro residues. The end product is a stable, homogeneous, high quality solid biofuel with far greater energy density and calorific value than the original feedstock. This provides significant benefits in logistics, handling and storage. It also opens up a wide range of potential uses for biomass.
Basic Torrefaction Principle
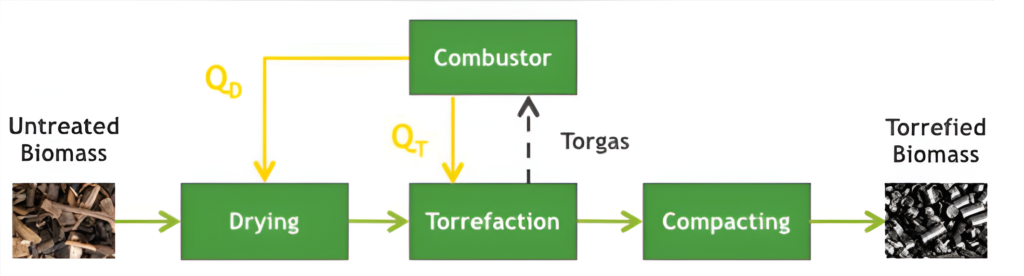
Biomass torrefaction involves heating the biomass to temperatures between 250 and 320 degrees Celsius in a low-oxygen atmosphere. When biomass is heated at such temperatures,
the moisture evaporates and various low-calorific components (volatiles) contained in the biomass are driven out. During this process mainly the hemi-cellulose in the biomass decomposes. This transforms the biomass from a fibrous low quality fuel into a product with excellent fuel characteristics.

Typically the torrefaction process results in a mass loss (dry basis) of 20-30% and an energy loss of 10-15%. To make a biomass torrefaction plant economically viable it is crucial to use the energy released in the volatiles. This can be done by burning the volatiles (torgas) in a lean gas combustor. The combustor can provide the heat for the drying and torrefaction. When the input feedstock has a moisture content of 35-45% the torrefaction process can be run auto-thermal. At higher mopisture content extra support fuel is needed to produce all the energy needed for the drying process.
1.2. Key Features of Torrefied Biomass:
• Moisture content: Less than 5%
• Calorific value: 4,800 to 5,200 kcal/kg
• High energy density and improved combustion
• Uniform in size and quality, suitable for automated feeding systems
2. Why Torrefied Biomass Is Ideal for Industry Heating?
Industries that rely on high-temperature heating—such as cement, steel, textiles, and chemicals—require fuels that offer consistent performance, energy density, and combustion stability. Torrefied biomass meets these criteria while offering environmental and economic advantages.
2.1. Major Benefits:
• Cleaner Combustion: Significantly lower SOx, NOx, and particulate emissions compared to coal or furnace oil.
• Carbon Neutral: Since biomass absorbs CO₂ during growth, its net emissions are near zero when sustainably sourced.
• Cost Savings: Offers stable pricing and long-term cost advantages over fluctuating fossil fuel prices.
• Drop-In Compatibility: This can be used in many existing combustion systems with minimal modification.
• Better Handling: Unlike raw biomass, torrefied fuel is dry, non-sticky, and easier to transport and store.

3. Torrefied pellets are the ideal coal replacement
Torrefaction of biomass results in a high grade biofuel which can be used as a replacement of coal in electricity and heat production. Torrefied biomass can also be used as input for gasification processes in the production of high value biobased fuels and chemicals.
• Grinds & burns like coal – existing coal infrastructure can be used
• Lower feedstock costs
• Lower shipping and transport costs
• Minimal de-rating of the power plant
• Provides non-intermittent renewable energy
• Lower sulfur and ash content (compared with coal)

4. Applications of Torrefied Biomass in Heavy Industry
Torrefied biomass can be effectively used in a wide range of industrial heating processes, including:
• Boiler Systems: As a direct replacement for coal in steam generation.
• Thermic Fluid Heaters: For uniform high-temperature heating in textile, food, and chemical industries.
• Furnaces and Kilns: Especially in ceramics, metal forging, and cement plants.
• Gasifiers and Co-firing Systems: For hybrid energy systems combining biomass and other fuels.
5. Fuel Supply and Automation Compatibility
Torrefied biomass is available in pellet or briquette form, making it compatible with modern auto-fuel feeding systems and smart combustion controls. Unlike raw biomass, its consistent shape and density allow seamless integration into automated boiler systems.
6. Policy Support and Incentives for Biomass Fuels
The Indian government supports biomass adoption under multiple programmes such as:
• National Bio-Energy Programme (MNRE): Financial assistance for biomass power and heating
• Pollution Control Regulations: Favoring low-emission fuels
• State-Level Subsidies: For retrofitting boilers to use clean fuels
This regulatory environment makes the transition to biomass feasible and financially attractive.
7. Conclusion: Torrefied Biomass Is the Fuel for a Cleaner Industrial Future
Industrial heating needs are not going away—but fossil fuels should. With its coal-like performance, lower emissions, and compatibility with modern systems, torrefied biomass offers a compelling path forward for industries serious about sustainability.
It is already proving a reliable and affordable solution for cement kilns to textile heaters. For industries planning their next energy move, now is the time to consider switching to torrefied biomass and unlock long-term operational and environmental gains.





